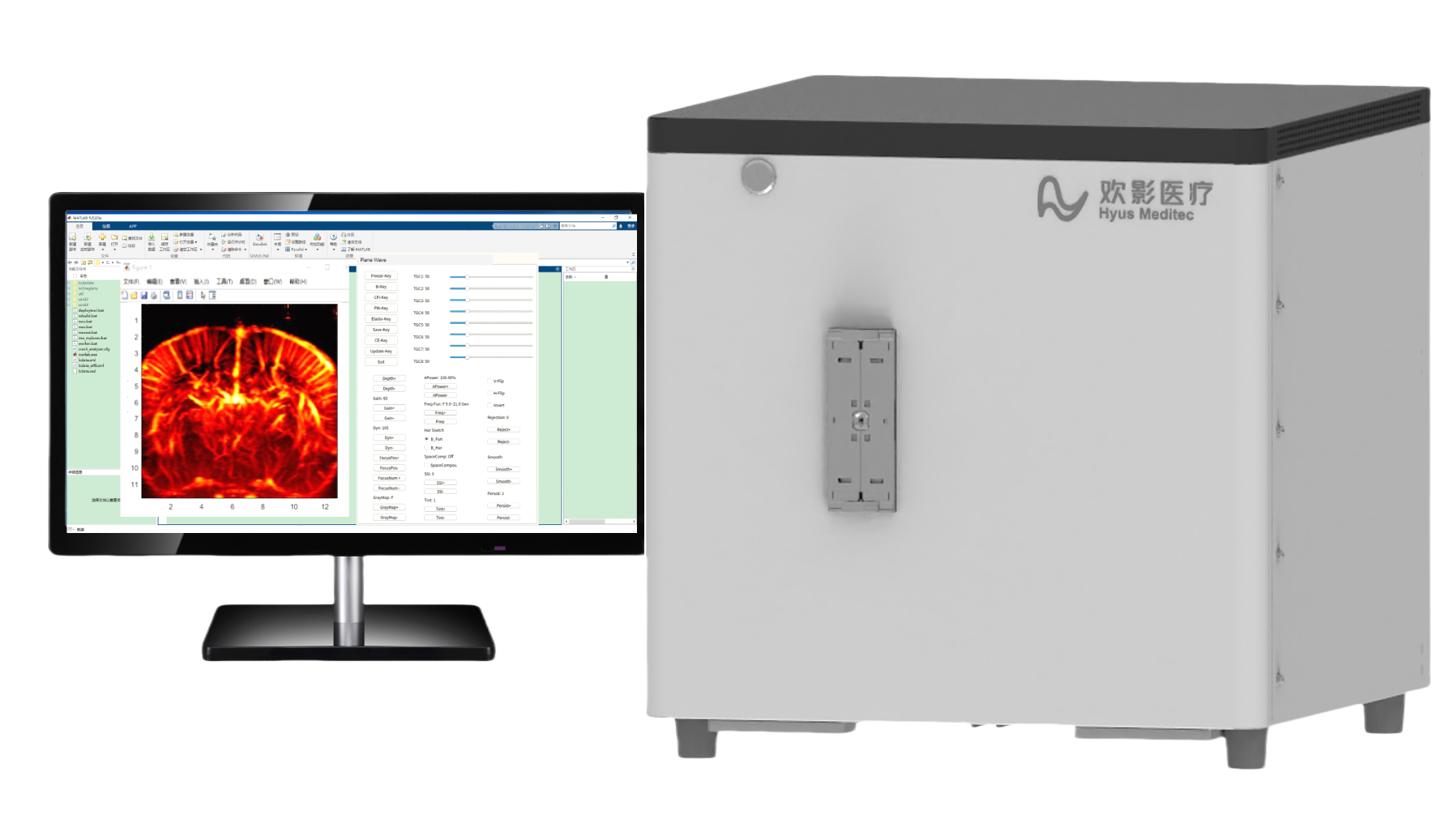
Functional Ultrasound (fUS)
Functional Ultrasound (fUS) Imaging is a high-sensitivity, high-resolution neuroresearch tool that achieves whole-brain functional imaging by detecting microvascular hemodynamic changes. With micron-scale spatial resolution and millisecond-level temporal resolution, it precisely correlates neural activity with blood flow dynamics, providing a novel approach for neuroscience research and brain disease modeling.

Functional Ultrasound (fUS)
Functional Ultrasound (fUS) Imaging is a high-sensitivity, high-resolution neuroresearch tool that achieves whole-brain functional imaging by detecting microvascular hemodynamic changes. With micron-scale spatial resolution and millisecond-level temporal resolution, it precisely correlates neural activity with blood flow dynamics, providing a novel approach for neuroscience research and brain disease modeling.
-
Ultra-High Sensitivity Imaging
·Detects microvascular-scale blood flow signals
·Contrast-agent-free, based on ultra-fast ultrasound technology
Whole-Brain Dynamic Monitoring
·Enables awake animal brain research(compatible with head-mounted probes)
·Supports multi-modal integration with photoacoustic imaging/EEG
Precision Neural Activation Mapping
·Generates functional brain atlases via sensory/behavioral/electrical stimulation
·Deciphers neurovascular coupling mechanisms
-
Neural Circuit Research
· Maps activation patterns across olfactory/visual/auditory sensory pathways
· Tracks interregional coordination during learning/memory processes
Brain Disease Model Analysis
· Alzheimer's Disease: Monitors hemodynamic abnormalities in amyloid plaque deposition regions
· Stroke Model: Evaluates hemodynamic changes in ischemic penumbra
· Epilepsy Model: Tracks ictal hyperperfusion propagation pathways
Precision Neural Activation Mapping
· Correlates spontaneous behaviors with specific brain region activation
· Decodes neural encoding mechanisms of social behaviors
-
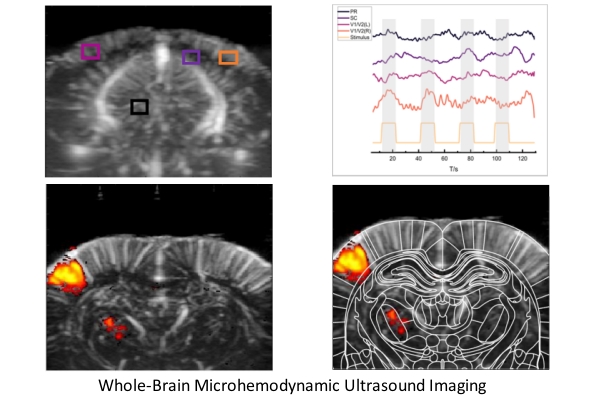
Rodent Whisker Stimulation Experiment
The novel fUS (functional ultrasound) brain imaging technology enables real-time tracking of neural activation evoked by whisker stimulation in rats. Square waves represent whisker stimuli, while blue areas depict cerebral blood volume (CBV) responses captured by fUS. The acquired CBV signals correlate with stimulation cycles, demonstrating synchronous activation in somatosensory cortex regions. During stimulation, fUS signals show ~30% amplitude increase, confirming its capability to capture stimulus-evoked brain activity.
-

Primate Visual Stimulation Experiment
The novel fUS (functional ultrasound) brain imaging technology enables real-time tracking of cerebral blood volume (CBV) responses in visual cortex regions during diverse visual pattern stimulation.